Lesson 1 - Introduction
US Lesson 1 Part 1 and 2 - Computer Basics and Textbook Basics
US Lesson 1 Part 5 - Introduction and Creating Your DoDEA Network Password
Last week you logged-in to your DoDEA student Gmail account using a Chromebook. Today, you will be a Dell laptop computer to sign-in to to the DoDEA network. All students will have to set a password (even if you were here last year). The user name for the network is the same as your Gmail user name.
DoDEA Network Password Requirements
- Passwords must be at least nine characters in length.
- Passwords must include at least one number
- Passwords must include at least one upper-case letter
- Passwords must include at least one lower-case letter
US Lesson 1 Part 3 - Overview and Introduction
US Lesson 1 Part 4 - Important Dates Related to US History (Part I of II)
These five dates span the period that you will be studying this year in US History. All five dates are very important in the history of the United States. Learn the dates and the important events that are associated with them. Note- There will be a quiz next week that will cover this important information.
These five dates span the period that you will be studying this year in US History. All five dates are very important in the history of the United States. Learn the dates and the important events that are associated with them. Note- There will be a quiz next week that will cover this important information.
1492 Italian sailor Columbus Arrives in the America (Columbus sailed the
ocean blue in 1492)
1607 English settlers arrive at Jamestown (modern day Virginia)
1775-1783 American Revolution (American colonists battled the British for
independence)
July 4, 1776 Declaration of Independence (signed at Independence Hall in
Philadelphia, Pennsylvania)
1861-1865 American Civil War (between the North states and the Southern states)
ocean blue in 1492)
1607 English settlers arrive at Jamestown (modern day Virginia)
1775-1783 American Revolution (American colonists battled the British for
independence)
July 4, 1776 Declaration of Independence (signed at Independence Hall in
Philadelphia, Pennsylvania)
1861-1865 American Civil War (between the North states and the Southern states)
Lesson 2 - Early Americans
DoDEA Standards
7.1a Geography and climate influenced the migration and cultural development of Native Americans. Native Americans in North America settled into different regions and developed distinct cultures.
7.1a Geography and climate influenced the migration and cultural development of Native Americans. Native Americans in North America settled into different regions and developed distinct cultures.
- Students will compare and contrast different Native American culture groups of North America, with a focus on the influence geographic factors had on their development.
- Students will examine various groups of Native Americans located within the United States.
US Lesson 2 Part 1 - Introduction and Overview to Native Americans
Topic 1.1 The Early Americans (Pages 12-13)
Three Ways Native Americans Supported Themselves
The map on page 12 reflects the geographic regions where Native Americans lived in North America. The following are four of the areas shown on the map.
Major Concept – The Spanish, French, Dutch, and the British all settled in what we now call the United States of America.
Major Concept - The British pushed the Native Americans west as they settled new areas. This continued when the American Colonies declared their independence and became an independent country.
- foraging
- farming
- hunting
The map on page 12 reflects the geographic regions where Native Americans lived in North America. The following are four of the areas shown on the map.
- Eastern Woodlands (East Coast of the United States)
- Southeast (East Coast of the United States)
- Great Plains
- Southwest
Major Concept – The Spanish, French, Dutch, and the British all settled in what we now call the United States of America.
Major Concept - The British pushed the Native Americans west as they settled new areas. This continued when the American Colonies declared their independence and became an independent country.
US Lesson 2 Parts 2 and 3 - Native Americans and Regions Assignment
Work with your group to complete this assignment. Read each section aloud and then discuss the answers. Each student is responsible for writing the answers on their own papers. When you write the four sentences, be sure to use quotation marks for each of the sentences.
- Adapting to and Modifying Environments (page 14) - What is the central idea of this section?
- Cultures of the Eastern Woodlands Region (page 17) - What are the four most important sentences in section?
- Cultures of the Great Plains Region - What are the four most important sentences in section?
- Cultures of the Southwest Region - What are the two most important sentences in section?
- Cultures of the Southeast Region - What are the four most important sentences in section?
Lesson 3 - Celebrating the U.S. Constitution
DoDEA Standard 7.4 HISTORICAL DEVELOPMENT OF THE CONSTITUTION
The newly independent states faced political and economic struggles under the Articles of Confederation. These challenges resulted in a Constitutional Convention, a debate over ratification, and the eventual adoption of the Bill of Rights.
7.4b The lack of a strong central government under the Articles of Confederation presented numerous challenges. A convention was held to revise the Articles, the result of which was the Constitution. The Constitution established a democratic republic with a stronger central government.
SL.1 (Speaking and Listening) Engage effectively in a range of collaborative discussions (one-on-one, in groups, and teacher-led) with diverse partners on grade 7 topics, texts, and issues, building on others’ ideas and expressing their own clearly.
US Lesson 3 Parts 1 and 2 - 4.2 Drafting A Constitution
This week we will celebrate the supreme law of the land - the United States Constitution. Work with your group today and read this short chapter about the making of this important document. Discuss the chapter as you read and focus specifically on the Venn diagram on page 187.
The newly independent states faced political and economic struggles under the Articles of Confederation. These challenges resulted in a Constitutional Convention, a debate over ratification, and the eventual adoption of the Bill of Rights.
7.4b The lack of a strong central government under the Articles of Confederation presented numerous challenges. A convention was held to revise the Articles, the result of which was the Constitution. The Constitution established a democratic republic with a stronger central government.
SL.1 (Speaking and Listening) Engage effectively in a range of collaborative discussions (one-on-one, in groups, and teacher-led) with diverse partners on grade 7 topics, texts, and issues, building on others’ ideas and expressing their own clearly.
US Lesson 3 Parts 1 and 2 - 4.2 Drafting A Constitution
This week we will celebrate the supreme law of the land - the United States Constitution. Work with your group today and read this short chapter about the making of this important document. Discuss the chapter as you read and focus specifically on the Venn diagram on page 187.
|
Key Concepts
|
Three Branches of the Government Legislative Branch (Congress) Executive Branch (President and Cabinet) Judicial Branch (Supreme Court) What state did not attend the Constitutional Convention in 1787? Rhode Island Legislative Branch (Congress) House of Representatives (435 Members) Senate (100 Members) |
US Lesson 3 Parts 3 / 4 - 4.4 Federalists, Antifederalists, and the Bill of Rights
Work with your group today and read this chapter about the ratification and amending of this important document.
Key Question- What were the key issues in the constitutional debate?
Work with your group today and read this chapter about the ratification and amending of this important document.
Key Question- What were the key issues in the constitutional debate?
|
Key Concepts
|
Primary Source - Library of Congress
"Publius (pseudonym for James Madison). The Federalist. No. X in the New York Daily Advertiser, November 22, 1787. Serial and Government Publications Division (68.03.00) [Digital ID# vc6.7a]"
|
US Lesson 3 Part 5 - The Preamble
Lesson 4 - Celebrating the U.S. Constitution
DoDEA Standard 7.2 Colonial Developments
European exploration of the New World resulted in various interactions with Native Americans and in colonization. The American colonies were established for a variety of reasons and developed differently based on economic, social, and geographic factors. Colonial America had a variety of social structures under which not all people were treated equally.
European exploration of the New World resulted in various interactions with Native Americans and in colonization. The American colonies were established for a variety of reasons and developed differently based on economic, social, and geographic factors. Colonial America had a variety of social structures under which not all people were treated equally.
DoDEA Standard 7.4 HISTORICAL DEVELOPMENT OF THE CONSTITUTION
The newly independent states faced political and economic struggles under the Articles of Confederation. These challenges resulted in a Constitutional Convention, a debate over ratification, and the eventual adoption of the Bill of Rights.
7.4b The lack of a strong central government under the Articles of Confederation presented numerous challenges. A convention was held to revise the Articles, the result of which was the Constitution. The Constitution established a democratic republic with a stronger central government.
US Lesson 4 Parts 1, 2, and 3 - 4.5 Understanding the U.S. Constitution
This week we will continue to celebrate the supreme law of the land - the United States Constitution. Work with your group today and read this short chapter about the making of this important document. Discuss the chapter as you read and focus specifically on the responsibilities of each of the three branches.
Article I - Article I defines the structure and responsibilities of the Legislative Branch of the government (Congress). The primary responsibility of Congress is to make the laws of the nation.
Article II - Article II of the Constitution defines the Executive Branch and the duties of the President. The President’s primary responsibility is to enforce the laws of the nation.
Article III - Article III of the Constitution defines the responsibilities of the judicial branch of government. The Supreme Court's primary responsibility is to ensure that the nation's laws are constitutional.
The newly independent states faced political and economic struggles under the Articles of Confederation. These challenges resulted in a Constitutional Convention, a debate over ratification, and the eventual adoption of the Bill of Rights.
7.4b The lack of a strong central government under the Articles of Confederation presented numerous challenges. A convention was held to revise the Articles, the result of which was the Constitution. The Constitution established a democratic republic with a stronger central government.
US Lesson 4 Parts 1, 2, and 3 - 4.5 Understanding the U.S. Constitution
This week we will continue to celebrate the supreme law of the land - the United States Constitution. Work with your group today and read this short chapter about the making of this important document. Discuss the chapter as you read and focus specifically on the responsibilities of each of the three branches.
Article I - Article I defines the structure and responsibilities of the Legislative Branch of the government (Congress). The primary responsibility of Congress is to make the laws of the nation.
Article II - Article II of the Constitution defines the Executive Branch and the duties of the President. The President’s primary responsibility is to enforce the laws of the nation.
Article III - Article III of the Constitution defines the responsibilities of the judicial branch of government. The Supreme Court's primary responsibility is to ensure that the nation's laws are constitutional.
Lesson 5 - U.S. Constitution Wrap-Up
DoDEA Standard 7.4 HISTORICAL DEVELOPMENT OF THE CONSTITUTION
The newly independent states faced political and economic struggles under the Articles of Confederation. These challenges resulted in a Constitutional Convention, a debate over ratification, and the eventual adoption of the Bill of Rights.
7.4b The lack of a strong central government under the Articles of Confederation presented numerous challenges. A convention was held to revise the Articles, the result of which was the Constitution. The Constitution established a democratic republic with a stronger central government.
The newly independent states faced political and economic struggles under the Articles of Confederation. These challenges resulted in a Constitutional Convention, a debate over ratification, and the eventual adoption of the Bill of Rights.
7.4b The lack of a strong central government under the Articles of Confederation presented numerous challenges. A convention was held to revise the Articles, the result of which was the Constitution. The Constitution established a democratic republic with a stronger central government.
|
US Lesson 5 Parts 1 and 2 - Bill of Rights Assignment This week we will wrap-up our study of the United States Constitution of 1787. |
Today's assignment will help you to learn about the Bill of Rights and help you to prepare for the test. Use the paper provided to complete this assignment. Begin by placing the heading (name, date, and "Mr. Duncan P-"_) in the upper-left-hand corner of the page. Draw lines to create ten boxes on the paper. In each box, write the name of each of the ten amendments in the Bill of Rights. Then, use a sentence or two to describe the main focus of each of the ten amendments. Finally, draw a large picture in each box that reflects or symbolizes each of the amendments. Use color and make the overall appearance as neat as possible. This class assignment is due tomorrow at the end of class. Use the link provided here and the textbook to help you to complete this assignment.
US History Test - U.S. Constitution (Wednesday)
US Lesson 5 Parts 3 and 5 - Text Reading Assignment 1.3 European Exploration in the Americas (Pages 33-40)
Today you will be reading with cooperative reading group. Read the assigned section aloud and focus particularly on the Columbian Exchange. The graphic on page 39 is very useful in understanding the Columbian Exchange. Be sure to discuss what is being exchanged between the Western Hemisphere and Eastern Hemisphere.
Writing Assignment - After completing the read assignment and group discussion, each person in the group will complete the following assignment. Use a sheet of notebook paper to make a list with two columns. Title the left column "Western Hemisphere" and the right column "Eastern Hemisphere." First, list as many plants, animals, diseases, and inventions that originated in the Western Hemisphere. Next, list as many plants, animals, diseases, and inventions that originated in the Eastern Hemisphere. All of the items in your lists must come from the textbook. Keep discussing the possibilities with your group and adding to your list until five minutes before the bell. Submit your assignment in the "Inbox" before you leave class.
Today you will be reading with cooperative reading group. Read the assigned section aloud and focus particularly on the Columbian Exchange. The graphic on page 39 is very useful in understanding the Columbian Exchange. Be sure to discuss what is being exchanged between the Western Hemisphere and Eastern Hemisphere.
Writing Assignment - After completing the read assignment and group discussion, each person in the group will complete the following assignment. Use a sheet of notebook paper to make a list with two columns. Title the left column "Western Hemisphere" and the right column "Eastern Hemisphere." First, list as many plants, animals, diseases, and inventions that originated in the Western Hemisphere. Next, list as many plants, animals, diseases, and inventions that originated in the Eastern Hemisphere. All of the items in your lists must come from the textbook. Keep discussing the possibilities with your group and adding to your list until five minutes before the bell. Submit your assignment in the "Inbox" before you leave class.
|
Assignment
Use the paper provided in class to create a visual display of the Columbian Exchange. You may attempt to recreate the graphic that was used in the video or create your own design. Include plants, animals, diseases, and inventions that originated in both the Western and Eastern Hemispheres. Be sure to label the hemispheres, the Atlantic Ocean, and the continents. Make the visual display colorful, interesting, and readable. This assignment is due at the end of next class period. |
US Lesson 6 - 2.1 Spanish Colonization and New Spain
DoDEA Standard 7.2 Colonial Developments
European exploration of the New World resulted in various interactions with Native Americans and in colonization. The American colonies were established for a variety of reasons and developed differently based on economic, social, and geographic factors. Colonial America had a variety of social structures under which not all people were treated equally.
7.2a Social, economic, and scientific improvements helped European nations launch an Age of Exploration.
SL.1 (Speaking and Listening) Engage effectively in a range of collaborative discussions (one-on-one, in groups, and teacher-led) with diverse partners on grade 7 topics, texts, and issues, building on others’ ideas and expressing their own clearly.
European exploration of the New World resulted in various interactions with Native Americans and in colonization. The American colonies were established for a variety of reasons and developed differently based on economic, social, and geographic factors. Colonial America had a variety of social structures under which not all people were treated equally.
7.2a Social, economic, and scientific improvements helped European nations launch an Age of Exploration.
SL.1 (Speaking and Listening) Engage effectively in a range of collaborative discussions (one-on-one, in groups, and teacher-led) with diverse partners on grade 7 topics, texts, and issues, building on others’ ideas and expressing their own clearly.
US Lesson 6 Part 1 - Columbian Exchange Part II Assignment
Use the paper provided in class to create a visual display of the Columbian Exchange. You may attempt to recreate the graphic that was used in the video or create your own design. Include plants, animals, diseases, and inventions that originated in both the Western and Eastern Hemispheres. Be sure to label the hemispheres, the Atlantic Ocean, and the continents. Make the visual display colorful, interesting, and readable. This assignment is due at the end of class today.
Use the paper provided in class to create a visual display of the Columbian Exchange. You may attempt to recreate the graphic that was used in the video or create your own design. Include plants, animals, diseases, and inventions that originated in both the Western and Eastern Hemispheres. Be sure to label the hemispheres, the Atlantic Ocean, and the continents. Make the visual display colorful, interesting, and readable. This assignment is due at the end of class today.
US Lesson 6 Parts 2 / 3 / 4 - Primary Sources / 2.1 Spanish Colonization and New Spain
US Lesson 6 Writing Assignment - Spain in the Americans Assignment
Complete the writing assignment using your textbook as your information source. Answer each question using complete sentences and provide evidence from the text to support your answers. All answers require you to restate the question, provide evidence in the form of a quote (and page number), and comment on the evidence. This assignment has been assigned to you in Google Classroom. Remember that you can access the online text by using ClassLink.
Complete the writing assignment using your textbook as your information source. Answer each question using complete sentences and provide evidence from the text to support your answers. All answers require you to restate the question, provide evidence in the form of a quote (and page number), and comment on the evidence. This assignment has been assigned to you in Google Classroom. Remember that you can access the online text by using ClassLink.
US Lesson 7 - 2.2 First French, Dutch, and English Colonies
DoDEA Standard 7.2 Colonial Developments- European exploration of the New World resulted in various interactions with Native Americans and in colonization. The American colonies were established for a variety of reasons and developed differently based on economic, social, and geographic factors. Colonial America had a variety of social structures under which not all people were treated equally.
7.2c European nations established colonies in North America for economic, religious, and political reasons. Differences in climate, physical features, access to water, and sources of labor contributed to the development of different economies in the New England, Middle, and Southern Colonies.
7.2d The Dutch established settlements along the Hudson River and the French established settlements in the Champlain Valley. Dutch contributions to American society were long-lasting.
7.2c European nations established colonies in North America for economic, religious, and political reasons. Differences in climate, physical features, access to water, and sources of labor contributed to the development of different economies in the New England, Middle, and Southern Colonies.
7.2d The Dutch established settlements along the Hudson River and the French established settlements in the Champlain Valley. Dutch contributions to American society were long-lasting.
|
US Lesson 7 Part 1 Finish - Spain in the Americans Assignment
Complete the writing assignment using your textbook as your information source. Answer each question using complete sentences and provide evidence from the text to support your answers. All answers require you to restate the question, provide evidence in the form of a quote (and page number), and comment on the evidence. |
This assignment has been assigned to you in Google Classroom. This assignment is due at the end of class.
US Lesson 7 Part 2 - 2.2 The First French, Dutch , and English Colonies
US Lesson 7 Part 2 - 2.2 The First French, Dutch , and English Colonies
Enduring Understandings
- The French and Dutch also colonized North America, seeking to profit from the fur trade.
- English colonists settled along the east coast of North America.
- People seeking religious freedom founded New England's colonies, as well as Pennsylvania and Maryland.
- The slave trade brought enslaved Africans to the English colonies, especially in the South, which relied on slavery for plantation agriculture.
- The English colonies developed representative government and inherited a tradition of legal rights from England.
|
US Lesson 7 Part 4 Text Reading Assignment - 2.2 European Rivalries / New France Is Colonized
So far we have focused on the Spanish and their colonization of the Americas. Now, we will shift our focus to the eastern coast of the United States and Canada learn how other European countries settled the Americas. The French established their first permanent settlement in 1605 and it was called New France. Work with your cooperative learning group to read and discuss pages 56-60. Pay particular attention to the map on page 58. Report out when you group is ready to describe what you read. As you read, focus on the question below. Focus Questions
|
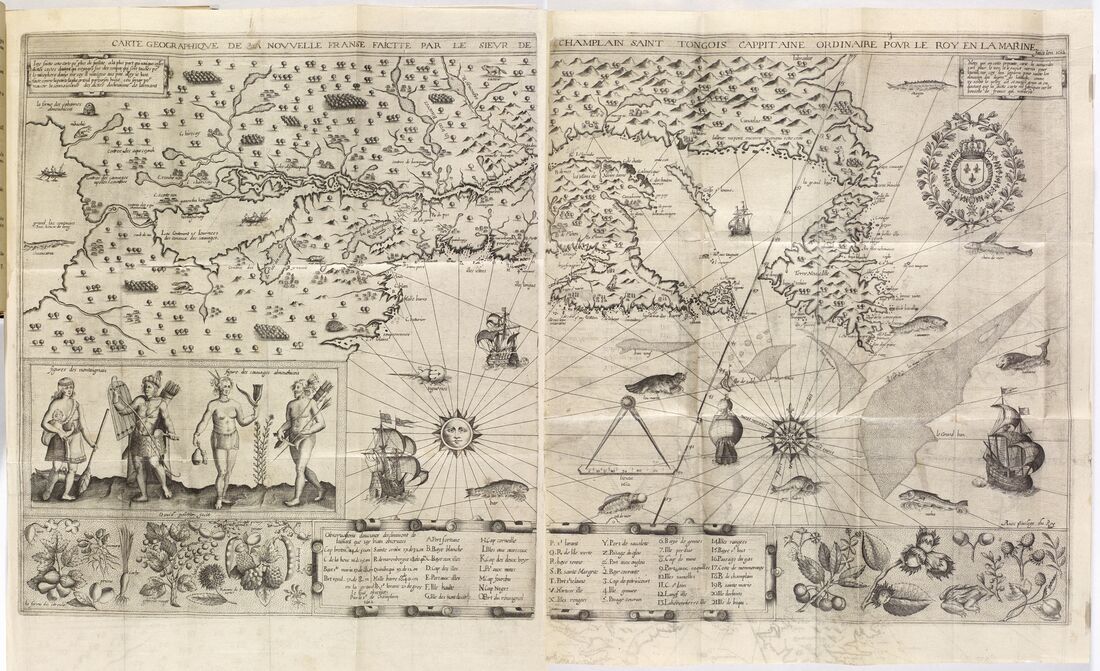
Geographical Map of New France Made by Mr. de Champlain (1603 Voyage)
Source- Library of Congress
Source- Library of Congress
Samuel de Champlain departed his home country of France in 1603. Forty days later he arrived in modern-day Canada. During his expedition he traveled up the St. Lawrence River and arrived near modern-day Montreal. He later established Quebec City in 1608.
US Lesson 8 - 2.2 First French, Dutch, and English Colonies
DoDEA Standard 7.2 Colonial Developments- European exploration of the New World resulted in various interactions with Native Americans and in colonization. The American colonies were established for a variety of reasons and developed differently based on economic, social, and geographic factors. Colonial America had a variety of social structures under which not all people were treated equally.
7.2c European nations established colonies in North America for economic, religious, and political reasons. Differences in climate, physical features, access to water, and sources of labor contributed to the development of different economies in the New England, Middle, and Southern Colonies.
7.2d The Dutch established settlements along the Hudson River and the French established settlements in the Champlain Valley. Dutch contributions to American society were long-lasting.
7.2c European nations established colonies in North America for economic, religious, and political reasons. Differences in climate, physical features, access to water, and sources of labor contributed to the development of different economies in the New England, Middle, and Southern Colonies.
7.2d The Dutch established settlements along the Hudson River and the French established settlements in the Champlain Valley. Dutch contributions to American society were long-lasting.

US Lesson 8 Part 1 Text Reading Assignment - 2.2 The Dutch Colonization of North America
Overview- The Dutch began to settle at the mouth of the Hudson River and nearby areas just a few decades after the French settled in North America.
2.2 Reading Assignment - Work with your cooperative learning group to read and discuss pages 60-62. Report out when you group is ready to describe what you read. As you read, focus on the question below.
2.2 CER Writing Assignment
Complete the writing assignment using your textbook as your information source. Answer each question using complete sentences and provide evidence from the text to support your answers. All answers require you to restate the question, provide evidence in the form of a quote (and page number), and comment on the evidence. This assignment has been assigned to you in Google Classroom. Remember that you can access the online text by using ClassLink. This assignment is due tomorrow morning at 8:00.
Overview- The Dutch began to settle at the mouth of the Hudson River and nearby areas just a few decades after the French settled in North America.
2.2 Reading Assignment - Work with your cooperative learning group to read and discuss pages 60-62. Report out when you group is ready to describe what you read. As you read, focus on the question below.
2.2 CER Writing Assignment
Complete the writing assignment using your textbook as your information source. Answer each question using complete sentences and provide evidence from the text to support your answers. All answers require you to restate the question, provide evidence in the form of a quote (and page number), and comment on the evidence. This assignment has been assigned to you in Google Classroom. Remember that you can access the online text by using ClassLink. This assignment is due tomorrow morning at 8:00.
- What English explorer is credited with discovering the Hudson River and when did it occur?
- Who purchased Manhattan Island from the Native Americans?
- What was the Dutch settlement on Manhattan Island called?
- How did Dutch colonization of the Americas differ from French colonization?
Henry Hudson entering New York Bay, September 11, 1609, with Indian family watching on shore in foreground
Source- Library of Congress
Source- Library of Congress
US Lesson 8 Part 2 - Special Activity
US Lesson 8 Part 2 - Special Activity
Format
Homework- Assigned in Class
- Save the file as “2021 10 US Lesson 8 Part 2 Last Name”
- Type the questions in bold.
- Answer the questions below it using complete sentences (without putting them in bold).
- Use evidence and page numbers to support all answers (use the proper format).
- Complete a spelling and grammar check of the assignment before submitting it for a grade.
- Submit the assignment in Google Classroom.
- All students must complete their assignments by the end of class or complete it for homework.
- All computers must be cleaned and put away prior to the end of class.
Homework- Assigned in Class
US Lesson 9 - 2.2 English Colonies
DoDEA Standard 7.2 Colonial Developments- European exploration of the New World resulted in various interactions with Native Americans and in colonization. The American colonies were established for a variety of reasons and developed differently based on economic, social, and geographic factors. Colonial America had a variety of social structures under which not all people were treated equally.
7.2c European nations established colonies in North America for economic, religious, and political reasons. Differences in climate, physical features, access to water, and sources of labor contributed to the development of different economies in the New England, Middle, and Southern Colonies.
7.2c European nations established colonies in North America for economic, religious, and political reasons. Differences in climate, physical features, access to water, and sources of labor contributed to the development of different economies in the New England, Middle, and Southern Colonies.

US Lesson 9 Part 1 Reading Assignment - 2.2 English Settlements in North America
Work with your cooperative learning group to read and discuss pages 62-68. Report out when you group is ready to describe what you read. As you read, focus on the question below.
Questions
Work with your cooperative learning group to read and discuss pages 62-68. Report out when you group is ready to describe what you read. As you read, focus on the question below.
Questions
- Why did Jamestown colony have so little food in its early years?
- What crop helped Jamestown's economy to improve after 1612?
- What was the name of the first legislative assembly in the English colonies?
- Why does the text state that "At first free Virginians had even greater rights that citizens in England"?
- What Bacon's Rebellion? What caused it?
- What impact did Virginia's lifelong enslavement laws have on Africans in the colony?






















